Colon Polyps
Topic Overview
What are colon polyps?
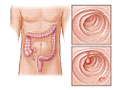
Colon polyps are growths in your large intestine (colon). The cause of most colon polyps is not known, but they are common in adults.
Over time, some polyps can turn into colorectal cancer. It usually takes many years for that to happen.
What are the symptoms?
You can have colon polyps and not know it, because they usually don’t cause symptoms. They are usually found during routine screening tests for colorectal cancer. A screening test looks for signs of a disease when there are no symptoms.
If polyps get large, they can cause symptoms. You may have bleeding from your rectum or a change in your bowel habits. A change in bowel habits includes diarrhea, constipation, going to the bathroom more often or less often than usual, or a change in the way your stool looks.
How are colon polyps diagnosed?
Most polyps are found during tests for colorectal cancer. Experts recommend routine colorectal cancer testing for most adults around age 50 who have a normal risk for colorectal cancer. People with a higher risk, such as those with a strong family history of colorectal cancer, may need to be tested sooner. The tests for colorectal cancer include stool tests that can be done at home and procedures, such as a colonoscopy, that are done at your doctor’s office or clinic.
What increases your risk of getting colon polyps?
You are more likely to have colon polyps if:
- You are over 50.
- Colon polyps or colorectal cancer runs in your family.
- You inherited a certain gene that causes you to develop polyps. People with this gene are much more likely than others to get the kind of polyps that turn into colorectal cancer.
How are they treated?
Doctors usually remove colon polyps, because some of them can turn into colorectal cancer. Most polyps are removed during a colonoscopy. You may need to have surgery if you have a large polyp.
After you have had polyps, you have a higher chance of developing new polyps. If you have had polyps removed, it is important to have follow-up testing to look for more polyps. Talk to your doctor about how often you need to be tested.
Health Tools
Health Tools help you make wise health decisions or take action to improve your health.
Symptoms
Colon polyps usually do not cause symptoms unless they are larger than 1 cm (0.4 in.) or they are cancerous. The most common symptom is rectal bleeding. Sometimes the bleeding may not be obvious (occult) and may only be discovered after doing a screening test for blood in the stool.
Colon polyps usually do not cause pain or a change in bowel habits unless they are large and are blocking part of the colon. These symptoms are rare, because polyps usually are discovered and removed before they become large enough to cause problems.
After cancer develops, additional symptoms may occur, such as changes in bowel habits and significant weight loss.
Exams and Tests
Unless colon polyps are large and cause bleeding or pain, the only way to know if you have polyps is to have one or more tests that explore the inside surface of your colon.
Several tests can be used to detect colon polyps. Two of these exams, flexible sigmoidoscopy and colonoscopy, also can be used to collect tissue samples (called a biopsy) or to remove colon polyps. All the tests may be used to screen for colon polyps and colorectal cancer and as follow-up tests after colon polyps have been removed. There are two basic types of tests—stool tests and tests that look inside your body.
Stool tests
- Fecal immunochemical test (FIT) is done to look for microscopic amounts of blood in the stool. There aren’t any restrictions on what you can eat before having this test. If the test is positive for blood in the stool, it is important to have a colonoscopy. This will help your doctor find the source of the blood and remove polyps if they are found.
- Guaiac fecal occult blood test (gFOBT) also looks for blood in the stool, but it isn’t as specific as the FIT. There are restrictions on what you can eat before having this test. If this test is positive for blood in the stool, you will need to have a colonoscopy.
- Stool DNA test (sDNA/Cologuard) looks at DNA in the stool to see if there are changes in the cells of the colon. Certain kinds of changes in cell DNA happen when you have cancer. If your test is abnormal, you will need to have a colonoscopy.
An abnormal result from a stool test doesn’t mean that you have colorectal cancer. It might be a false-positive result. So the next step is to have a colonoscopy. After you’ve had the colonoscopy, you and your doctor will know whether or not you have cancer.
Tests that look inside your body
- Flexible sigmoidoscopy allows the doctor to look at the lower third of the colon. During a sigmoidoscopy exam, samples of any growths can be collected (biopsied). And precancerous and cancerous polyps can sometimes be removed. But if your doctor finds polyps, you will need to have a colonoscopy to check the upper part of your colon.
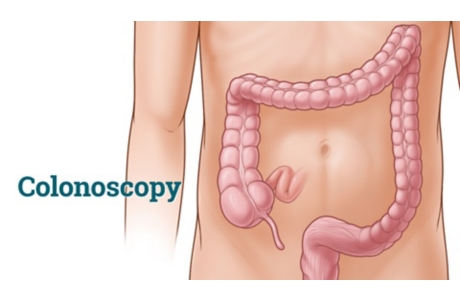
- Colonoscopy lets the doctor inspect the entire colon for polyps and cancer. During a colonoscopy, samples of any growths can be collected (biopsied). And precancerous and cancerous polyps usually can be removed.
- CT colonography (virtual colonoscopy) uses X-rays to make a detailed picture of the colon to help the doctor look for polyps. If this test finds polyps, you will need to have a colonoscopy.
Screening for colorectal cancer
Screening for colorectal cancer reduces your chance of having complications and dying from colorectal cancer. Your risk for colorectal cancer gets higher as you get older. Some experts say that adults should start regular screening at age 50 and stop at age 75. Others say to start before age 50 or continue after age 75. Talk with your doctor about your risk and when to start and stop screening.
Screening options include the following commonly used tests.
- Stool-based tests. These tests can be done at home.
- FIT (fecal immunochemical test) is done every year.
- gFOBT (guaiac fecal occult blood test) is done every year.
- sDNA (stool DNA) is done every 3 years.
- Direct-view tests. These tests are done in your doctor’s office or clinic.
- Colonoscopy is done every 10 years.
- CT colonography is done every 5 years.
- Flexible sigmoidoscopy is done every 5 years. Or you can have this test every 10 years if you also do the FIT every year.
The method of screening that you have depends on your personal preferences, your doctor’s preferences, and what the clinic or office you go to is able to do.
People with a higher risk for colorectal cancer, such as those with a strong family history of colorectal cancer, may need to be tested earlier than most adults. Others who may need to be tested earlier include those with a family history of familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP) or Lynch syndrome, also known as hereditary nonpolyposis colon cancer (HNPCC).
Talk with your doctor. Decide with him or her when to start and stop screening for colorectal cancer. These decisions will depend on how old you are, your family history, any health problems you have, and the benefits you can expect from regular screening.
Follow-up testing
If a biopsy of polyps obtained during screening reveals only hyperplastic polyps of any size, routine follow-up screening is all that is needed. These polyps do not become cancerous.
Most doctors agree that if you have had one or more adenomatous polyps removed, you probably need regular follow-up colonoscopy exams every few years. How often you need a colonoscopy may depend on the number and size of the polyps, your age, your health, and other risk factors that you may have for polyps. Talk with your doctor about the follow-up testing schedule that is right for you.
Treatment Overview
Polyps are removed during screening if you have a colonoscopy. The polyp is examined to find out if it is the kind that could become cancer.
Initial treatment
If adenomatous polyps are found during an exam with flexible sigmoidoscopy, a colonoscopy will be done to look for and remove any polyps in the rest of the colon.
The bigger a colon polyp is, especially if it is larger than 1 cm (0.4 in.), the more likely it is that the polyp will be adenomatous or contain cancer cells.
If only hyperplastic polyps are found during your flexible sigmoidoscopy, you likely do not need to have a colonoscopy. These polyps do not become cancerous. In this case you can continue your regular screenings, unless you are at an increased risk for colorectal cancer because of a family history of colorectal cancer or an inherited polyp syndrome.
A sessile polyp doesn’t have a stalk. It is mostly a flat growth. Like other colon polyps, it grows on the inside wall of the colon. Sessile polyps can turn into cancer. Like other polyps, they are removed if found during sigmoidoscopy or colonoscopy.
Risks of removing polyps during colonoscopy
Complications from colonoscopy are rare. There is a slight risk of:
- Puncturing the colon or causing severe bleeding by damaging the wall of the colon. (This happens in less than 3 out of 1,000 people having a colonoscopy.footnote 2, footnote 3)
- Bleeding caused by removing a polyp.
- Complications from sedatives given during the procedure.
Ongoing treatment
Regular screenings for colon polyps are the best way to prevent polyps from developing into colorectal cancer.
Most colon polyps can be identified and removed during a colonoscopy.
If you have had one or more adenomatous polyps removed, you probably need regular follow-up colonoscopy exams every 3 to 5 years. Talk with your doctor about the follow-up schedule that he or she thinks is best for you.
Treatment if the condition gets worse
Surgery is sometimes needed for large colon polyps that have a broad area of attachment (sessile polyps) to the colon wall. These large polyps sometimes cannot be removed safely during a colonoscopy and may be more likely to develop into cancer.
If cancer is found when the colon polyps are examined, you will begin treatment for colorectal cancer. For more information, see the topic Colorectal Cancer.
Home Treatment
No home treatment is done for colon polyps. See Treatment Overview for more information.
But you can take action that may prevent colon polyps:
- Stay at a healthy body weight.
- Quit smoking.
- Use alcohol in moderation. Moderate alcohol use usually is defined as 1 alcoholic beverage a day for women and 2 for men.
Experts are not yet certain that these approaches prevent colon polyps or colorectal cancer.
These self-care methods should not be a substitute for regular colorectal screening, especially if you are older than 50 or are at increased risk for colon polyps or colorectal cancer. While these approaches may decrease your risk for colon polyps, they will not prevent you from ever having colon polyps.
References
Citations
- U.S. Preventive Services Task Force (2016). Screening for colorectal cancer: U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommendation statement. JAMA, 315(23): 2564–2575. DOI:10.1001/jama.2016.5989. Accessed June 27, 2016.
- Warren JL, et al. (2009). Adverse events after outpatient colonoscopy in the Medicare population. Annals of Internal Medicine, 150(12): 849–857. DOI: 10.7326/0003-4819-150-12-200906160-00008. Accessed February 2, 2015.
- Rabeneck L, et al. (2008). Bleeding and perforation after outpatient colonoscopy and their risk factors in usual clinical practice. Gastroenterology, 135(6): 1899–1906. DOI 10.1053/j.gastro.2008.08.058. Accessed February 13, 2015.
Other Works Consulted
- Bresalier RS (2010). Colorectal cancer. In M Feldman et al., eds. Sleisenger and Fordtran’s Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease, 9th ed., vol. 2, pp. 2191–2238. Philadelphia: Saunders.
- Lieberman DA, et al. (2012). Guidelines for colonoscopy surveillance after screening and polypectomy: A consensus update by the U.S. Multi-Society Task Force on Colorectal Cancer. Gastroenterology, 143(3): 844–857.
- Rex DK, et al. (2009). American College of Gastroenterology guidelines for colorectal cancer screening 2008. American Journal of Gastroenterology, 104(3): 739–750.
- Syngal S, Katrinos F (2012). Colorectal cancer screening. In NJ Greenberger et al., eds., Current Diagnosis and Therapy: Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Endoscopy, 2nd ed., pp. 273–286. New York: McGraw-Hill.
- U.S. Preventive Services Task Force (2008). Screening for colorectal cancer: U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommendation statement. Available online: http://www.uspreventiveservicestaskforce.org/uspstf/uspscolo.htm.
Current as of: December 19, 2018
Author: Healthwise Staff
Medical Review:E. Gregory Thompson MD – Internal Medicine & Kathleen Romito MD – Family Medicine & Adam Husney MD – Family Medicine & Jerome B. Simon MD, FRCPC, FACP – Gastroenterology
This information does not replace the advice of a doctor. Healthwise, Incorporated, disclaims any warranty or liability for your use of this information. Your use of this information means that you agree to the Terms of Use. Learn how we develop our content.