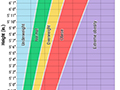
Body Mass Index (BMI)
Topic Overview
Your body mass index (BMI) and waist size affect your risk of type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and coronary artery disease. The following table shows the risk.
Body mass index (BMI) and the risk for diseasesfootnote 1
|
Classification
|
BMI
|
Waist size and relative risk
|
|
Men: less than 40 in. (102 cm)
Women: less than 35 in. (88 cm)
|
Men: 40 in. (102 cm) or more
Women: 35 in. (88 cm) or more
|
|
Normal
|
18.5–24.9
|
—
|
Increased risk
|
|
Overweight
|
25–29.9
|
Increased risk
|
High risk
|
|
Obesity I
|
30–34.9
|
High risk
|
Very high risk
|
|
Obesity II
|
35–39.9
|
Very high risk
|
Very high risk
|
|
Obesity III (extreme)
|
40 or above
|
Extremely high risk
|
Extremely high risk
|
For Asian people, each risk category may include lower BMIs than those listed in the table.
A BMI under 18.5 is considered unhealthy. There is risk that you are not getting sufficient nutrition (malnutrition). Complications of malnutrition include anemia, nutrient deficiency, heart irregularities, loss of menstrual periods in women (amenorrhea), cavities, and osteoporosis.
References
Citations
- National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, National Institutes of Health (2000). The Practical Guide: Identification, Evaluation, and Treatment of Overweight and Obesity in Adults (NIH Publication No. 00-4084). Available online: http://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/guidelines/obesity/prctgd_c.pdf.
Credits
Current as ofMarch 28, 2019
Author: Healthwise Staff
Medical Review: E. Gregory Thompson, MD – Internal Medicine
Kathleen Romito, MD – Family Medicine
Martin J. Gabica, MD – Family Medicine
Rhonda O’Brien, MS, RD, CDE – Certified Diabetes Educator
Current as of: March 28, 2019
Author: Healthwise Staff
Medical Review:E. Gregory Thompson, MD – Internal Medicine & Kathleen Romito, MD – Family Medicine & Martin J. Gabica, MD – Family Medicine & Rhonda O’Brien, MS, RD, CDE – Certified Diabetes Educator
National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, National Institutes of Health (2000). The Practical Guide: Identification, Evaluation, and Treatment of Overweight and Obesity in Adults (NIH Publication No. 00-4084). Available online: http://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/guidelines/obesity/prctgd_c.pdf.