Breastfeeding
Topic Overview
What is breastfeeding?
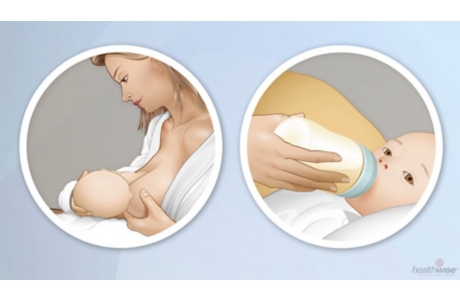
Breastfeeding is feeding a baby milk from the mother’s breasts. You can feed your baby right at your breast. You can also pump your breasts and put the milk in a bottle to feed your baby. Doctors advise breastfeeding for 1 year or longer. But your baby benefits from any amount of breastfeeding you can do.
Breast milk is the only food most babies need until about 6 months of age. You do not need to give your baby food, water, or juice. Ask your doctor when you can start feeding your baby solid foods. You will gradually breastfeed less often as your baby starts to eat other foods. But keep breastfeeding for as long as you and your child want to. Your baby continues to get health benefits from breast milk past the first year.
Breastfeeding lowers your child’s risk for sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS).footnote 2 Breast milk may also help protect your child from some health problems, such as infections, obesity, and diabetes.footnote 2
Breastfeeding has benefits for you too. You may recover from pregnancy, labor, and delivery sooner if you breastfeed. You may also lower your risk for certain health problems, such as breast cancer.footnote 3
Can all women breastfeed?
Almost all mothers of newborns are able to breastfeed. Even if you have a health problem, such as diabetes, or if you have had breast surgery, you can likely still breastfeed. But some women should not breastfeed, such as those who are HIV-positive or have active tuberculosis.
Breastfeeding is a learned skill—you will get better at it with practice. Be patient with yourself and your baby. If you have trouble, doctors, nurses, and lactation consultants can all help. So can friends, family, and breastfeeding support groups.
How do you plan for breastfeeding?
Before your baby is born, plan ahead. Learn all you can about breastfeeding. This helps make breastfeeding easier.
- Early in your pregnancy, talk to your doctor or midwife about breastfeeding.
- Learn the basics of breastfeeding before your baby is born. The staff at hospitals and birthing centers can help you find a lactation specialist. Or you can take a breastfeeding class.
- Plan ahead for times when you will need help after your baby is born. Many women get help from friends and family or they join a support group to talk to other breastfeeding mothers.
- Buy breastfeeding equipment, such as breast pads, nipple cream, extra pillows, and nursing bras. Find out about breast pumps, too.
How do you breastfeed?
For each feeding, you go through these basic steps:
- Get ready for the feeding. Be calm and relaxed, and try not to be distracted. Get some water or juice for yourself. And have two or three pillows to help support your baby while he or she is nursing.
- Find a breastfeeding position that is comfortable for you and your baby, such as the cross-cradle or the football hold. Make sure the baby’s head and chest are lined up straight and facing your breast. It’s best to switch which breast you start with each time.
- Get the baby latched on properly. Your baby’s mouth needs to be wide open, like a yawn, so you may need to gently touch the middle of your baby’s lower lip. When your baby’s mouth is open wide, quickly bring the baby onto your nipple and areola (the dark circle around your nipple).
- Provide a complete feeding. Let your baby decide how long to nurse. Be sure to burp your baby after each breast.
Talk to your doctor right away if you are having problems and aren’t sure what to do. Don’t be afraid to call even if you don’t quite know what it is that is bothering you. Your doctor is used to parents of newborns calling. He or she can help you figure out if there is a problem, and if so, how to fix it.
How often do you need to feed your baby?
Feed your baby whenever he or she is hungry. In the first 2 weeks, your baby will breastfeed about every 1 to 3 hours. That often works out to about 8 to 12 times in a 24-hour period. This schedule can make you very tired. But know that your baby will soon start eating more at each feeding, and you won’t need to breastfeed as often.
Plan for times when you will be apart from your baby. Use a breast pump to collect breast milk ahead of time. You can store milk in the refrigerator or freezer for times when someone else will be taking care of your baby. Experts usually recommend waiting about a month until breastfeeding is going well before offering a bottle.
Do you need to limit what you eat and drink?
Anything you put in your body can be passed to your baby in breast milk. If you are breastfeeding, don’t take drugs. Before you take any kind of medicine, herb, or vitamin, ask your doctor if it is safe.
If you are breastfeeding, limit alcohol. There isn’t a lot of research about exactly how much alcohol can harm a baby. Having no alcohol is the safest choice for your baby. If you choose to have a drink now and then, have only one drink, and limit the number of occasions that you have a drink. Wait to breastfeed at least 2 hours after you have a drink to reduce the amount of alcohol the baby may get in the milk.footnote 1
Be sure to eat healthy, balanced meals and snacks to get enough of the vitamins and minerals you need while breastfeeding. You need to eat extra calories and may need to keep taking your prenatal vitamins.
If you have questions about what to eat and what to avoid, talk with your doctor or midwife.
Health Tools
Health Tools help you make wise health decisions or take action to improve your health.
Benefits of Breastfeeding
Breastfeeding is a natural way to nourish your baby. It benefits both you and your baby. But it’s your decision whether to breastfeed.
Benefits for the baby
Breast milk provides your baby with vitamins and minerals for optimal growth and development. It also has the needed proteins, fats, and other substances for growth.
Breastfeeding provides health benefits for your baby, such as:
- Antibodies to strengthen your baby’s immune system.
- A lower risk for many types of infections, such as ear infections.
- Fewer gastrointestinal illnesses (vomiting and diarrhea).footnote 3
- A reduced risk for sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS).footnote 2
- A reduced risk for certain conditions, like diabetes.footnote 3
- A reduced risk for becoming obese later in infancy and during childhood.footnote 2
To compare, baby formula does not help protect a baby from infections and other health problems.
Benefits for the mother
Soon after your baby is born, breastfeeding helps your body recover from the stresses of pregnancy, labor, and delivery. Breastfeeding also stimulates your body to release oxytocin, which helps your uterus contract, bleed less, and return more quickly to its prepregnancy size.
Breastfeeding also lowers your risk for certain health problems, such as breast cancer or diabetes later on.footnote 3
You may find that losing weight is easier with breastfeeding. But weight-loss rates after delivery vary among women.
Feeding your baby milk at the breast is convenient, because you have a food source that is ready at all times. You don’t have to do anything to prepare.
It’s your decision
Breastfeeding is a personal choice. How you feed your baby is your decision. Your thoughts and feelings about it are an important part of the decision.
Planning to Breastfeed
With proper planning, preparation, and support, most women are able to breastfeed successfully.
At your prenatal visits, talk to your doctor or midwife about your plans to breastfeed. He or she can help guide you through the planning and get you started after the baby is born. You may also be referred to a lactation consultant.
How to Breastfeed
To breastfeed properly and prevent problems, you will need to learn the basics of breastfeeding. You will want to get ready before each feeding and find a position that is comfortable for you and your baby. Doing this will help you get your baby to latch on, so that you can provide a complete feeding each time. If you do have trouble with breastfeeding, get support from family, friends, your doctor, or a lactation consultant.
Get ready for a feeding
Being ready for a feeding will help you relax. And being relaxed will help your let-down reflex, which occurs just before or soon after feeding begins. It’s helpful to wear a loose blouse or a shirt that can be raised easily. If you want more privacy, use a lightweight blanket over your shoulder and chest to cover your breasts and your baby.
It is likely that you will have to breastfeed around other people, even strangers, when you are feeding your baby on demand. In many states and on federal property, your right to breastfeed in public is protected by law.
To get ready, you can also do things like:
- Make sure the room is quiet and warm. Keep the room darkened. Bright light makes it hard for newborns to open their eyes.
- Keep something to drink nearby. Most women get thirsty as they breastfeed. Drink enough to satisfy your thirst.
- Use one or more pillows to support your arms and the baby. Support your back with a pillow, and use a stool to raise your feet. This will help you and your baby be more comfortable during feeding.
- Make sure your baby is alert. This will help you get your baby to latch on. You may need to wake your baby.
Find a position
Breastfeeding in the proper position will help your baby latch on and breastfeed correctly. There are several breastfeeding positions, such as the cradle hold, the football hold, and the side-lying position.
As you start to breastfeed, try different positions to find those that are most comfortable for you and your baby. For example, use the cross-cradle hold at one feeding, and then use the football hold at the next. Feeding in different positions may reduce nipple soreness. Also, start each new feeding with the opposite breast you started with at the last feeding. This routine helps you to empty each breast completely.
For more help with finding the best position, see the topic Breastfeeding Positions.
Get your baby latched on
A proper latch helps prevent problems such as sore nipples, blocked milk ducts, breast infections, and poor infant weight gain. An improper latch is painful and frustrating. It causes some women to stop breastfeeding.
The steps to get your baby latched on are about the same for all breastfeeding positions. Latching on in the cross-cradle position is an easy one to start with.
- Make sure the baby’s head and body are lined up straight, not turned to one side or tilted up or down while breastfeeding. For this position, you and your baby should be tummy to tummy. Your baby’s nose should be right in front of your nipple.
- Support and narrow your breast with one hand using a “U hold,” with your thumb on the outer side of your breast and your fingers on the inner side. You can also use a “C hold,” with all your fingers below the nipple and your thumb above it. Try the different holds to get the deepest latch for whichever breastfeeding position you use. Your other arm is behind your baby’s back, with your hand supporting the base of the baby’s head. Position your fingers and thumb to point toward your baby’s ears.
- You can touch your baby’s lower lip with your nipple to get your baby to open his or her mouth. Wait until your baby opens up really wide, like a big yawn. Then be sure to bring the baby quickly to your breast—not your breast to the baby. As you bring your baby toward your breast, use your other hand to support the breast and guide it into his or her mouth.
- Both the nipple and a large portion of the darker area around the nipple (areola) should be in the baby’s mouth. The baby’s lips should be flared outward, not folded in (inverted).
- Listen for a regular sucking and swallowing pattern while the baby is feeding. If you cannot see or hear a swallowing pattern, watch the baby’s ears, which will wiggle slightly when the baby swallows. If the baby’s nose appears to be blocked by your breast, bring your baby’s body closer to you. This will help tilt the baby’s head back slightly, so just the edge of one nostril is clear for breathing.
- When your baby is latched, you can usually remove your hand from supporting your breast and bring it under your baby to cradle him or her. Now just relax and breastfeed your baby.
If you need to take the baby off the breast (for example, to reposition), you will need to break the baby’s latch on your nipple. To break your baby’s latch, put one finger into the corner of his or her mouth. This will gently break the latch. Then you can start again. If you don’t break the latch before you remove the baby from your breast, your nipples may become sore, cracked, or bruised.
Provide a complete feeding
Let your baby feed until he or she is satisfied.
- Offer the other breast when the first breast feels empty and your baby sucks more slowly, pulls off, or loses interest. Usually your baby will continue breastfeeding but for less time than on the first breast.
- To burp your baby, gently pat your baby’s back to help him or her let out any swallowed air. After the baby burps, offer the breast again. Sometimes a baby will want to continue feeding after being burped.
- If your baby falls asleep before finishing breastfeeding, you may need to stimulate him or her to finish the feeding. After a while, you will learn your baby’s patterns and will know whether he or she needs rousing or has fed long enough.
To learn more about your baby’s feeding needs, see Feeding Patterns.
Find support
The first two weeks of breastfeeding usually are the most challenging. You may have other times when you need extra help. Know who you can contact, such as friends and family who have breastfed or a lactation consultant. Other support is available through local hospitals or clinics and support organizations, such as La Leche League.
Your Health and Nutrition
A healthy lifestyle—including having a balanced diet, getting plenty of rest, and being active—is important while you breastfeed. It can help you have more energy and reduce stress. It can also help you build a healthy milk supply.
It’s also important to know what to avoid. Anything you put in your body can be passed to your baby in breast milk.
Have a healthy diet
- Have a balanced diet so that you get the vitamins and minerals you need for breastfeeding. You’ll need to eat extra calories compared to the amount you ate when you weren’t breastfeeding. It’s a good idea to continue taking your prenatal vitamins while breastfeeding.
- Avoid quick weight loss. If you want to try to lose your pregnancy weight, lose it a little at a time so you don’t affect your breast milk.
Some moms notice that certain foods make their babies more fussy. You may want to keep track of what you eat and how your baby acts.
If you have special dietary needs, talk to a dietitian. He or she can help you plan healthy meals.
Balance activity and sleep
- Try to sleep and rest as well as you can. You likely will not have a normal schedule when you first start to breastfeed. But you can take naps and find time to rest for short periods throughout the day, such as when your baby sleeps.
- Be active. Exercise helps with weight loss, improves your energy level, and can help relieve stress.
Use medicine wisely
- Be careful taking medicine. Many medicines can affect your breast milk. Talk with your doctor before taking any over-the-counter or prescription medicines or herbs.
- Stay current on your immunizations. It’s okay to get routine immunizations while you are breastfeeding. They do not harm your baby.
Know what to avoid
- Avoid poisonous substances, such as fish that may contain mercury, that can be passed on to your baby through breast milk.
- Avoid drugs, alcohol, and tobacco. Any substance that you use while breastfeeding can be passed on to your baby.
Adjust to lifestyle changes
- Understand sexual changes. Sexual relationships with your partner can take time to begin again.
- Use birth control methods if you want to lower your pregnancy risk. Women who are breastfeeding can still become pregnant. But you are not likely to become pregnant in the first 6 months of exclusive breastfeeding (which means you are feeding your baby on demand and not using formula, food, or water to supplement his or her diet). After your baby is 6 months of age, you need to use a birth control method if you want to avoid pregnancy, regardless of whether you are breastfeeding exclusively.
Having a new baby and breastfeeding take time to get used to. Take it easy on yourself. Find ways to help yourself cope in the first few months. Learning more about how your baby will grow and change may be helpful to you too. For more information, see the topic Growth and Development, Newborn.
Feeding Patterns
Knowing your baby’s feeding habits and diaper-change patterns is important, especially during the first few months of breastfeeding. There are usually patterns to how often he or she feeds and how often you will need to change his or her diaper. You may also notice changes in how long each feeding lasts and begin to recognize signs that your baby is getting enough milk. As your baby gets older, you may add supplements and other foods and eventually you will reach the time for weaning.
How often and how long to feed
The general recommendation is to feed your baby on demand. This means that you breastfeed whenever you notice signs that your baby is hungry, such as when he or she is eagerly sucking on fingers or rooting. This strategy also helps you produce more milk and ensures that the baby is well nourished.
During the first 2 weeks, on-demand feedings usually occur every 1 to 3 hours (about 8 to 12 feedings in a 24-hour period). You may have to wake a sleepy baby to feed him or her in the first few days after birth. These early feedings often are short. Sometimes a newborn breastfeeds for only a few minutes on each breast or only on one breast. These feedings are important to increase your milk supply over the first few days. Let your baby decide how long to nurse. This allows your baby to get the foremilk, which has water and needed nutrients, and hindmilk, which has more fat and calories to satisfy your baby’s appetite. Over time, feeding sessions will become longer.
At around 3 months of age, feedings may become less frequent. Your baby is able to drink more milk at one time, and your milk supply naturally increases as your baby’s needs increase.
Needs typically increase during growth spurts. When your baby has a growth spurt, he or she may seem to be hungry more often. By feeding your baby on demand, you increase your milk supply. After about 2 to 4 days, you will have increased your milk supply at each feeding to satisfy your baby for a longer period. After the growth spurt, the number of feedings will then gradually decrease.
Signs that your baby is getting enough milk
It is common to wonder if your baby is getting enough milk. Most babies lose weight in the first several days after birth but regain it within a week or two. Weight gain is more rapid after mature milk is produced, about 10 to 15 days after you deliver your baby. After breastfeeding is established, your baby will also get more hindmilk, which provides additional fat and calories. Look for signs that your baby is getting enough milk, such as having regular dirty and wet diapers. If you still have concerns, see When to Call a Doctor.
If you aren’t sure if your baby is getting enough milk, talk to your doctor. He or she can help you to find the problem, if one exists. Don’t supplement your breastfed baby’s diet with formula unless your doctor recommends it. Extra feedings with formula can interfere with your breast milk production and may lead to early weaning.
When to start supplements or other food
Feeding your baby will change through the first year. When your baby reaches about 6 months of age, you can start adding other foods besides breast milk. Ask your doctor when you can start feeding your baby solid foods. The American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) recommends breastfeeding babies for at least the first year and giving only breast milk for the first 6 months.footnote 1
Doctors usually recommend against supplementing a breastfed baby’s diet with formula, food, or water during the first 6 months, even during a growth spurt. Supplementing can decrease your milk production. Early bottle feedings can also make it harder for your baby to latch on to your breast.
Although breastfed babies get excellent nutrition, they will probably need certain vitamin or nutritional supplements to maintain or improve their health. For example, breastfed babies need vitamin D and may also require iron supplements. Talk with your doctor about how much and what sources of supplements are right for your child.
Signs of weaning
It’s best for you and your baby if you breastfeed for a full year. If you keep breastfeeding beyond 1 year, your baby will continue to benefit. After the first year, look for signs that your baby is ready to wean, such as refusing to breastfeed or showing interest in drinking from a cup. Talk to your doctor if you have questions about weaning.
Whenever you decide to wean, keep in mind that suddenly stopping breastfeeding may be harder for both you and your baby than a gradual decrease in feeding frequency.
To learn more about weaning, see the topic Weaning.
Pumping and Storing
Pumping and storing your milk allows you to breastfeed while working or just getting some time away from your baby. It’s a good idea to have a plan for when you’ll need to pump, select the right breast pump for you, and know how to store milk safely. These will help set you and your baby up for long-term breastfeeding success.
- Plan ahead to breastfeed at work. Planning can help you sort through details, such as where you can pump and how often you’ll need to pump. Regular pumping will ensure that your breasts produce enough milk and will keep your breasts from becoming uncomfortable and engorged.
- Select a breast pump. There are many types of pumps that you can get. You’ll want to think about which kind is most practical for how often you’ll need to use it.
- Store breast milk properly. Stored breast milk is the next best thing to fresh breast milk. But you’ll need to know how to safely prepare breast milk for storage and how long you can keep it.
Pumping and your milk supply
If you often feed your baby pumped breast milk, your milk supply may decrease. This is because your body releases less prolactin than it does when you feed your baby at the breast. To help keep your milk supply when you pump frequently:
- Breastfeed your baby whenever possible. For example, if you are working, breastfeed your baby frequently before you go to work in the morning, in the evening, and throughout the weekends.
- Keep a regular pumping schedule. Don’t try to make up for missing a session by pumping longer at the next one. This can lead to breast engorgement and decreased milk production.
- Use a double electric pump, which expresses milk from both breasts at the same time.
- Talk to a lactation consultant about how to manage a decreasing milk supply.
Common Problems
You may sometimes doubt your ability to successfully breastfeed. It’s common to have questions and struggles sometimes. You may notice that your baby is having problems. Or you may have problems during feeding or problems with your breasts. Remember, most breastfeeding issues are easily resolved when you know what to expect and have support from others, including your doctor, midwife, or lactation consultant.
Problems in babies
- Cold or flu. When your baby has a minor illness, such as a cold or the flu, continue breastfeeding. Breast milk is still the best nourishment.
- Digestive problems.Some foods may affect your breast milk and contribute to intestinal gas or other digestive problems. If you suspect that your baby’s crying gets worse after a feeding of breast milk, keep a record of what you eat and how your baby acts, especially when crying episodes occur. Some babies develop a cow’s milk sensitivity. If this occurs, stop including milk and dairy products in your diet, and talk to your doctor.
- Spitting up. Almost all babies spit up, especially newborns. Spitting up usually doesn’t seem to cause the baby any discomfort. But if your baby spits up more often, cries, acts fussy, or has trouble eating, there may be a problem called gastroesophageal reflux.
If you have other concerns or aren’t sure if you should see your baby’s doctor, see When to Call a Doctor.
Feeding babies with special conditions
Some babies are born with problems that interfere with their ability to breastfeed right away. But many of these babies can be fed breast milk using special techniques, such as cup-feeding or a feeding device called a supplemental nursing system. Feeding a premature baby or a baby with cleft palate or cleft lip may be challenging. Your doctor or a lactation consultant can guide you on feeding techniques.
Problems during feeding
- Latching on. Sometimes it can be hard for your baby to latch on, but there are some techniques that can make latching on easier.
- Biting the nipple. When your baby’s primary teeth start to come in, usually between 6 and 12 months of age, you both have to make a few adjustments. Your baby may have a temporary loss of appetite because his or her mouth is sore. Teething babies may bite the breast, not knowing that it causes pain. Usually, a firm “no” and a stern expression are enough to control this behavior. It may also help to stop breastfeeding when your baby is finished actively nursing and then give him or her cold teething items to chew on.
- Poor let-down. Practice some relaxation techniques, eat properly, and drink plenty of fluids. And try to breastfeed in comfortable, quiet, and familiar spots.
- Arousal during feeding. Some women notice that they become aroused during breastfeeding. Although this sensation is similar to a sexual response, it isn’t sexually driven. It’s your body’s way of preparing for breastfeeding.
Problems in moms
- Being sick. You can keep breastfeeding when you have a minor illness (such as the flu or a cold). Try to rest as much as you can, and drink fluids. Talk to your doctor if you have any questions or concerns about breastfeeding when you are sick or if you need to take prescription or over-the-counter medicines for your symptoms.
- Feeling depressed. Breastfeeding problems can be exaggerated if you have postpartum depression. Many women have some feelings of depression in the first few weeks after childbirth. This is commonly known as the “baby blues,” and it usually resolves on its own. But some women’s bodies respond to changing postpartum hormone levels with a lasting depression that requires treatment. Talk to your doctor if your baby is more than a few weeks old and you continue to have trouble sleeping (insomnia) or concentrating, or if you often feel sad, tearful, anxious, hopeless, or irritable.
Breast problems
- Breast and nipple changes. Many women notice differences in how their breasts look and feel during breastfeeding. Early changes (such as larger breasts) are related to the body’s preparation for milk production. Other changes, such as a darker color and increased size of the areola (the dark circle around the nipple) and more prominent nipples, are sometimes permanent. Some women may have inverted nipples and may need help from a lactation consultant to get started with breastfeeding.
- Sore or cracked nipples. You can help relieve the pain from sore or cracked nipples by rubbing a few drops of breast milk on the nipple and areola and letting it air dry. You can also try applying pure lanolin cream on your nipples.
- Engorged breasts. You may have painful breasts and flattened nipples, making it hard for a baby to latch on for feeding. Gently massage your breasts and express or pump some milk to soften your nipple and areola before breastfeeding. This will help your baby latch deeper onto your breast, past your nipple and onto your areola. Wearing a supportive, well-fitting bra also may help. Applying cold compresses to your breasts now and then after breastfeeding may reduce swelling and pain. For more information, see the topic Breast Engorgement.
- Blocked milk ducts. Blocked milk ducts may cause a painful lump in the breast. Untreated blocked milk ducts can lead to an infection, which will require a visit to your doctor. Massage the affected area toward the nipple before breastfeeding and during feeding. This simple measure can help release the milk plug. Also, this is one time you should always feed your baby on the affected side first. Your baby is usually more eager at the start of a feeding. The stronger sucking force helps empty the breast and unblock the duct.
- Breast infections. These are treated with prescription medicines and home treatment. Infections that sometimes occur with breastfeeding include:
- A yeast infection, which may affect you and your baby. The baby often has white patches in his or her mouth (thrush) or a diaper rash, while your nipples may be extremely sore. You may also experience stabbing pains in your breast, especially as you start to breastfeed and in between feedings. You and your baby must both be treated with medicine, such as nystatin, for a yeast infection.
- Mastitis, which may cause a fever, flu-like symptoms, and pain in the breast with an inflamed, red, dimpled, or swollen area. An untreated infection may lead to an abscess, which can cause a firm, often painful mass in the breast. You may need to take an antibiotic medicine to treat the infection. For more information, see the topic Mastitis.
Most women can take acetaminophen (such as Tylenol) and ibuprofen (such as Advil) while breastfeeding to help relieve discomfort from some of these problems. But talk to your doctor before taking any medicine (prescription or nonprescription).
Milk problems
- Leaking breast milk. Your let-down reflex may be stimulated unintentionally. Be prepared by using absorbent pads that you change frequently. You can use washable or disposable pads, but don’t use pads that have a plastic backing.
- Low milk supply. More frequent breastfeeding usually helps increase the milk supply within 48 hours. You can also try pumping both breasts for 10 to 15 minutes each after you have just fed your baby. You should notice an increase in your milk supply after 2 to 4 days of the extra pumping. Other things can affect milk production, but it’s rare to have a true milk deficiency. Contact a lactation consultant if you think your milk supply is too low.
- Relactation. Relactation means stimulating your body to again produce breast milk and start breastfeeding or taking measures to stimulate your body to produce breast milk when you have not been pregnant recently (such as for an adopted baby).
If you have other concerns or aren’t sure if you should see your doctor, see When to Call a Doctor. For problems related to technique or positioning, you also can talk to or visit a lactation consultant.
When To Call a Doctor
Call your doctor now if you have:
- Increasing pain in one area of the breast.
- Increasing redness in one area of the breast or red streaks extending away from an area of the breast.
- Drainage of pus from the nipple or another area of the breast.
- A fever of 101°F (38.3°C) or higher.
Call your doctor today if you have:
- Breast problems, such as cracked and bleeding nipples or blisters on your nipples, that are not relieved by home treatment.
- A fever less than 101°F (38.3°C).
- Symptoms of postpartum depression, such as often feeling sad, tearful, anxious, hopeless, or irritable. Postpartum depression can make breastfeeding problems seem even worse.
- Swollen glands (lymph nodes) in the neck or armpit.
Call your doctor today if your baby:
- Is not eating well for any reason or has any of the following symptoms:
- A rectal temperature of 100.4°F (38°C) or higher
- Fussiness or sleepiness that interferes with breastfeeding
- Weakness, listlessness, or lack of interest in feeding
- Thick, white patches in the mouth and cheeks, which are signs of a yeast infection (thrush), or signs of a diaper rash
- Shows signs of poor eating, such as:
- Not reaching his or her birth weight by 2 weeks of age or other signs of insufficient weight gain.
- Having no wet diapers for 6 hours.
- Passing little or no stool over a 24-hour period in the first 4 weeks, or passing stools that are dark green and contain mucus after the first few days. But it is normal for your baby to have fewer stools starting around 4 to 8 weeks of age. As long as stools stay soft and your baby is feeding well, it should not be a concern.
- Having problems latching on to the breast.
References
Citations
- American Academy of Pediatrics (2012). Policy statement: Breastfeeding and the use of human milk. Pediatrics, 129(3): e827–e841. Also available online: http://pediatrics.aappublications.org/content/129/3/e827.full.
- Task Force on Sudden Infant Death Syndrome (2016). SIDS and other sleep-related infant deaths: Updated 2016 recommendations for a safe infant sleeping environment. Pediatrics, 138(5): e20162938. DOI: 10.1542/peds.2016-2938. Accessed October 24, 2016.
- Victoria CG, et al. (2016). Breastfeeding in the 21st century: Epidemiology, mechanisms, and lifelong effect. Lancet, 387(10017): 475-490. DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(15)01024-7. Accessed January 16, 2018.
- American Academy of Pediatrics (2009). Breastfeeding. In RE Kleinman, ed., Pediatric Nutrition Handbook, 6th ed., pp. 29–59. Elk Grove Village, IL: American Academy of Pediatrics.
Other Works Consulted
- American Academy of Pediatrics (2010). Diagnosis and prevention of iron deficiency and iron-deficiency anemia in infants and young children (0–3 years of age). Pediatrics, 126(5): 1040–1050. Available online: http://pediatrics.aappublications.org/cgi/content/full/126/5/1040.
- American Academy of Pediatrics (2014). Breastfeeding. In Pediatric Nutrition, 7th ed., pp. 41–59. Elk Grove Village, IL: American Academy of Pediatrics.
- American Academy of Pediatrics, American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (2012). Intrapartum and postpartum care of the mother. In Guidelines for Perinatal Care, 7th ed., pp. 169–210. Elk Grove, IL: American Academy of Pediatrics.
- American Academy of Pediatrics, Section on Breastfeeding (2005). Breastfeeding and the use of human milk. Pediatrics, 115(2): 496–506.
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (2007). Breastfeeding: Maternal and infant aspects. ACOG Committee Opinion No. 361. Obstetrics and Gynecology, 109(2 pt 1): 479–480.
- Haemer M, et al. (2014). Normal childhood nutrition and its disorders. In WW Hay Jr et al., eds., Current Diagnosis and Treatment: Pediatrics, 22nd ed., pp. 305–333. New York: McGraw-Hill.
- Martin RM, et al. (2005). Breastfeeding in infancy and blood pressure in later life: Systematic review and meta-analysis. American Journal of Epidemiology, 161(1): 15–26.
- Owen CG, et al. (2006). Does breastfeeding influence the risk of type 2 diabetes in later life? A quantitative analysis of published evidence. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 84: 1043–1054.
- Stuebe AM, et al. (2005). Duration of lactation and incidence of type 2 diabetes. JAMA, 294(20): 2601–2610.
- Wagner CL, et al. (2008). Prevention of rickets and vitamin D deficiency in infants, children, and adolescents. American Academy of Pediatrics Clinical Report. Pediatrics, 122(5): 1142–1152.
Current as of: May 29, 2019
Author: Healthwise Staff
Medical Review:Sarah Marshall MD – Family Medicine & John Pope MD – Pediatrics & Kathleen Romito MD – Family Medicine & Adam Husney MD – Family Medicine & Kirtly Jones MD – Obstetrics and Gynecology
This information does not replace the advice of a doctor. Healthwise, Incorporated, disclaims any warranty or liability for your use of this information. Your use of this information means that you agree to the Terms of Use. Learn how we develop our content.