Emphysema
Current as of: June 9, 2019
Author: Healthwise Staff
Medical Review:E. Gregory Thompson, MD – Internal Medicine & Adam Husney, MD – Family Medicine & Ken Y. Yoneda, MD – Pulmonology, Critical Care Medicine
Emphysema is a long-term (chronic) lung disease. In emphysema, the tiny air sacs (alveoli) at the end of the airways in the lungs are damaged. When the air sacs are damaged or destroyed, their walls break down and the sacs become larger. These larger air sacs move less oxygen into the blood. This causes difficulty…
Current as of: June 9, 2019
Author: Healthwise Staff
Medical Review:E. Gregory Thompson, MD - Internal Medicine & Adam Husney, MD - Family Medicine & Ken Y. Yoneda, MD - Pulmonology, Critical Care Medicine
06/09/2019
This information does not replace the advice of a doctor. Healthwise, Incorporated, disclaims any warranty or liability for your use of this information. Your use of this information means that you agree to the Terms of Use. Learn how we develop our content.

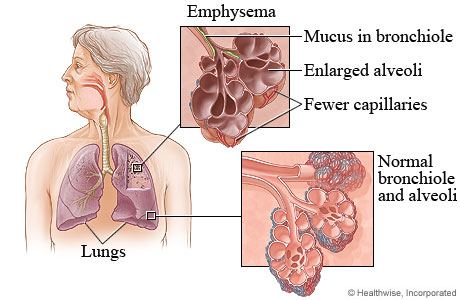
Emphysema is a long-term (chronic) lung disease. In emphysema, the tiny air sacs (alveoli) at the end of the airways in the lungs are damaged. When the air sacs are damaged or destroyed, their walls break down and the sacs become larger. These larger air sacs move less oxygen into the blood. This causes difficulty breathing or shortness of breath that gets worse over time. After air sacs are destroyed, they cannot be replaced.
Emphysema is a form of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). It is usually caused by smoking. A rare type of emphysema is caused by the lack of a substance in the lungs called alpha1-antitrypsin. This type of emphysema is usually inherited.
Current as of: June 9, 2019
Author: Healthwise Staff
Medical Review:E. Gregory Thompson, MD – Internal Medicine & Adam Husney, MD – Family Medicine & Ken Y. Yoneda, MD – Pulmonology, Critical Care Medicine
This information does not replace the advice of a doctor. Healthwise, Incorporated, disclaims any warranty or liability for your use of this information. Your use of this information means that you agree to the Terms of Use. Learn how we develop our content.
Current as of: June 9, 2019
Author: Healthwise Staff
Medical Review:E. Gregory Thompson, MD - Internal Medicine & Adam Husney, MD - Family Medicine & Ken Y. Yoneda, MD - Pulmonology, Critical Care Medicine
06/09/2019
This information does not replace the advice of a doctor. Healthwise, Incorporated, disclaims any warranty or liability for your use of this information. Your use of this information means that you agree to the Terms of Use. Learn how we develop our content.
