VBAC: Participation During Birth
Topic Overview
You and your birth partner can take part more fully in a vaginal birth than you can in a cesarean delivery.
During a cesarean, the mother gets either a regional anesthetic or a general anesthetic. She can’t fully take part in her baby’s birth.
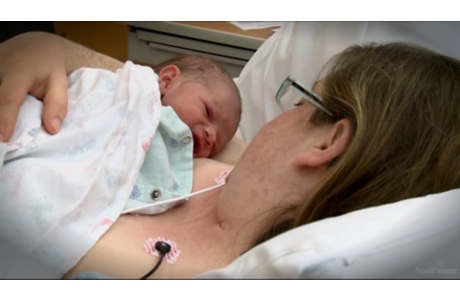
- Some mothers feel very strongly about being able to bond with the baby right after birth. Unless there is some complication, a mother can usually hold her baby within the first few minutes after a vaginal birth. After a cesarean, the mother’s time with her baby may be briefly delayed as her surgery is completed. This delay can be longer if she stays in the recovery room for a time after the birth.
- When a general anesthetic is used, the mother is unconscious through her baby’s birth. This most often happens during an emergency cesarean.
- If regional anesthetic is used during a cesarean, the mother stays awake. But she may not be as actively involved in the birth as during a natural birth or a birth without using medicines. If she gets sedatives, she may be groggy. Or she may fall asleep or not remember much about the birth.
Whether you plan a vaginal birth after cesarean (VBAC) or a repeat cesarean, discuss anesthesia options with your doctor before your delivery.
If you have a routine cesarean, your birth partner can hold the baby while your medical needs are taken care of.
Credits
Current as ofMay 29, 2019
Author: Healthwise Staff
Medical Review: Sarah Marshall MD – Family Medicine
Adam Husney MD – Family Medicine
Kathleen Romito MD – Family Medicine
Kirtly Jones MD – Obstetrics and Gynecology
Current as of: May 29, 2019
Author: Healthwise Staff
Medical Review:Sarah Marshall MD – Family Medicine & Adam Husney MD – Family Medicine & Kathleen Romito MD – Family Medicine & Kirtly Jones MD – Obstetrics and Gynecology